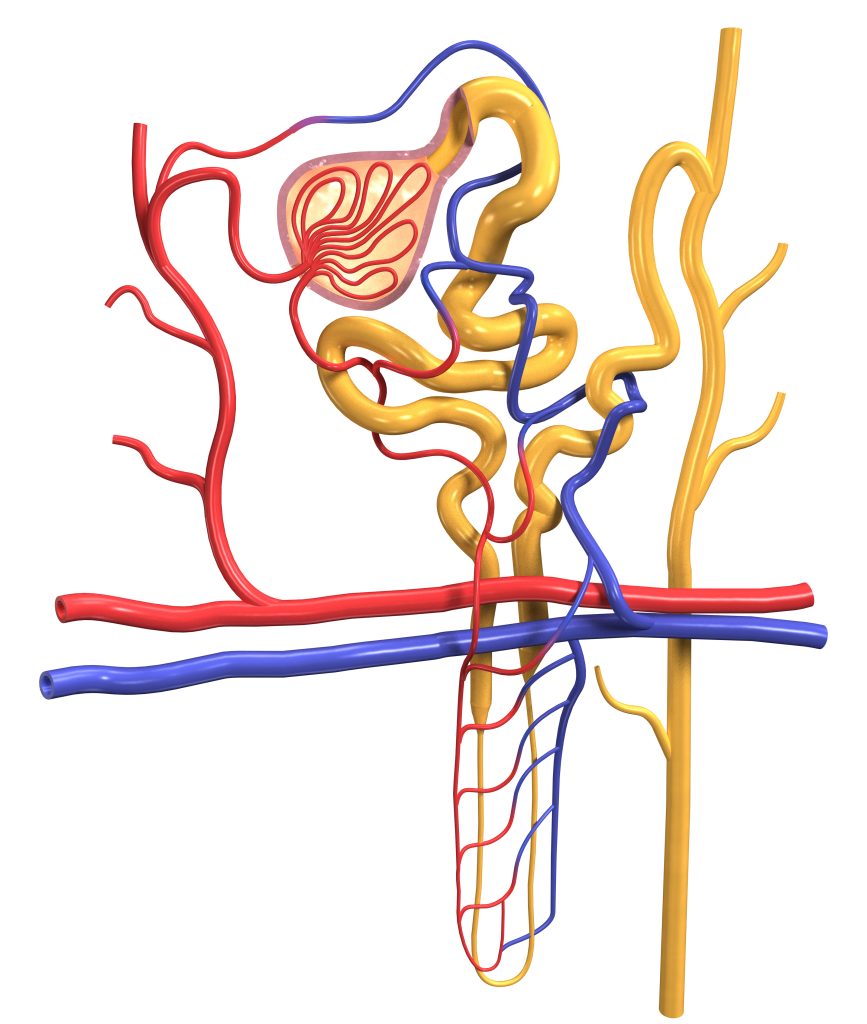
This image depicts the detailed structure of a nephron, the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and forming urine. Each kidney contains approximately one million nephrons, which work to remove waste products and excess substances from the bloodstream, maintaining the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance.
Key Components of the Nephron:
Glomerulus (Red):
- The glomerulus is a network of capillaries located within the Bowman’s capsule. It serves as the initial site of blood filtration. The blood pressure forces water, salts, glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules out of the blood and into the Bowman’s capsule, forming the filtrate.
Bowman’s Capsule (Pink Outline):
- This cup-shaped structure surrounds the glomerulus and collects the filtrate. The Bowman’s capsule leads into the renal tubule, where further processing of the filtrate occurs.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (Yellow):
- This is the first segment of the renal tubule, where a significant amount of reabsorption occurs. Essential substances such as glucose, amino acids, and ions are reabsorbed back into the blood from the filtrate.
Loop of Henle (Yellow):
- This U-shaped structure has a descending and ascending limb, which play critical roles in concentrating the urine. The descending limb allows water to be reabsorbed, while the ascending limb actively transports salts out of the filtrate.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (Yellow):
- This segment continues the process of reabsorption and secretion. It helps to fine-tune the composition of the urine by reabsorbing sodium and calcium while secreting potassium and hydrogen ions.
Collecting Duct (Yellow):
- The final segment where multiple nephrons empty their filtrate. It further concentrates the urine by reabsorbing water and is regulated by hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH). The urine then flows into the renal pelvis and ureter for excretion.
Blood Vessels (Red and Blue):
- The network of blood vessels shown includes the afferent arteriole (bringing blood to the glomerulus) and the efferent arteriole (carrying blood away from the glomerulus). Surrounding capillaries (peritubular capillaries and vasa recta) play a role in reabsorbing substances from the renal tubule back into the bloodstream.
This intricate system of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion ensures that the kidneys effectively cleanse the blood, regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, and maintain homeostasis.
Quiz
Please note that our articles are not intended to guide personal health decisions.
This content has been curated by Renes Care. Unauthorized use or reproduction is prohibited.
© Renes Care. All rights reserved.
