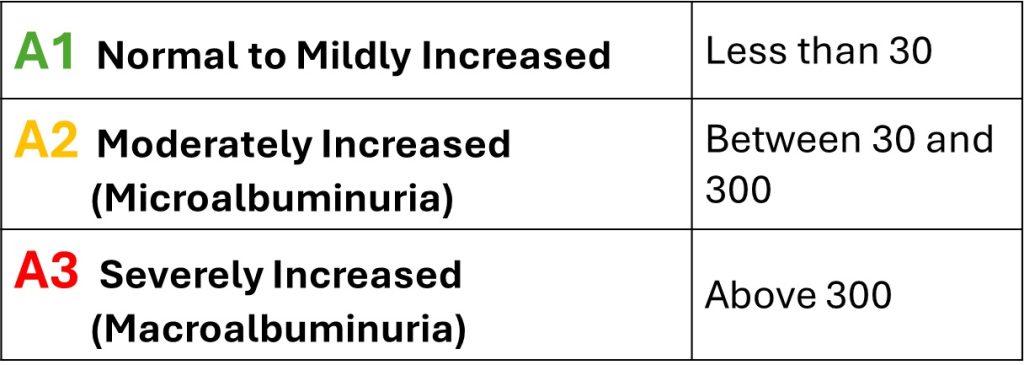
This table provides a classification system for albuminuria, a key marker for kidney health. Albuminuria measures the level of albumin, a type of protein, in urine. Elevated levels suggest kidney stress or damage and can help determine the severity of kidney disease. Here’s a detailed explanation of each category:
- A1 – Normal to Mildly Increased (Green):
- Urine Albumin Level: Less than 30 mg/g of creatinine.
- Interpretation: This is considered normal and reflects healthy kidney function or minimal kidney stress. No immediate concerns.
- Monitoring: Routine checkups are sufficient unless other risk factors for kidney disease are present.
- A2 – Moderately Increased (Yellow):
- Urine Albumin Level: Between 30 and 300 mg/g of creatinine.
- Known as: Microalbuminuria (small amounts of albumin in urine).
- Interpretation: This level often indicates early kidney damage, commonly caused by diabetes or hypertension. It’s a reversible stage if managed promptly with proper medical care, such as controlling blood sugar and blood pressure.
- Action: Requires lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and potentially starting medications to prevent further damage.
- A3 – Severely Increased (Red):
- Urine Albumin Level: Above 300 mg/g of creatinine.
- Known as: Macroalbuminuria (large amounts of albumin in urine).
- Interpretation: This suggests significant kidney damage, which may be irreversible. It can lead to chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression if left untreated.
- Action: Requires immediate medical intervention, comprehensive treatment plans, and monitoring by a nephrologist.
Why Is Albuminuria Important?
- It’s one of the earliest signs of kidney damage, often detectable before changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- Persistent albuminuria over time increases the risk of kidney failure and cardiovascular diseases.
Color Coding Significance:
- Green: Healthy or low risk.
- Yellow: Warning stage; intervention needed.
- Red: High risk; immediate action required.
This classification allows healthcare providers to identify early-stage kidney disease, guide treatment decisions, and monitor progression effectively. It’s a cornerstone of kidney disease management.
Please note that our articles are not intended to guide personal health decisions.
This content has been curated by Renes Care. Unauthorized use or reproduction is prohibited.
© Renes Care. All rights reserved.