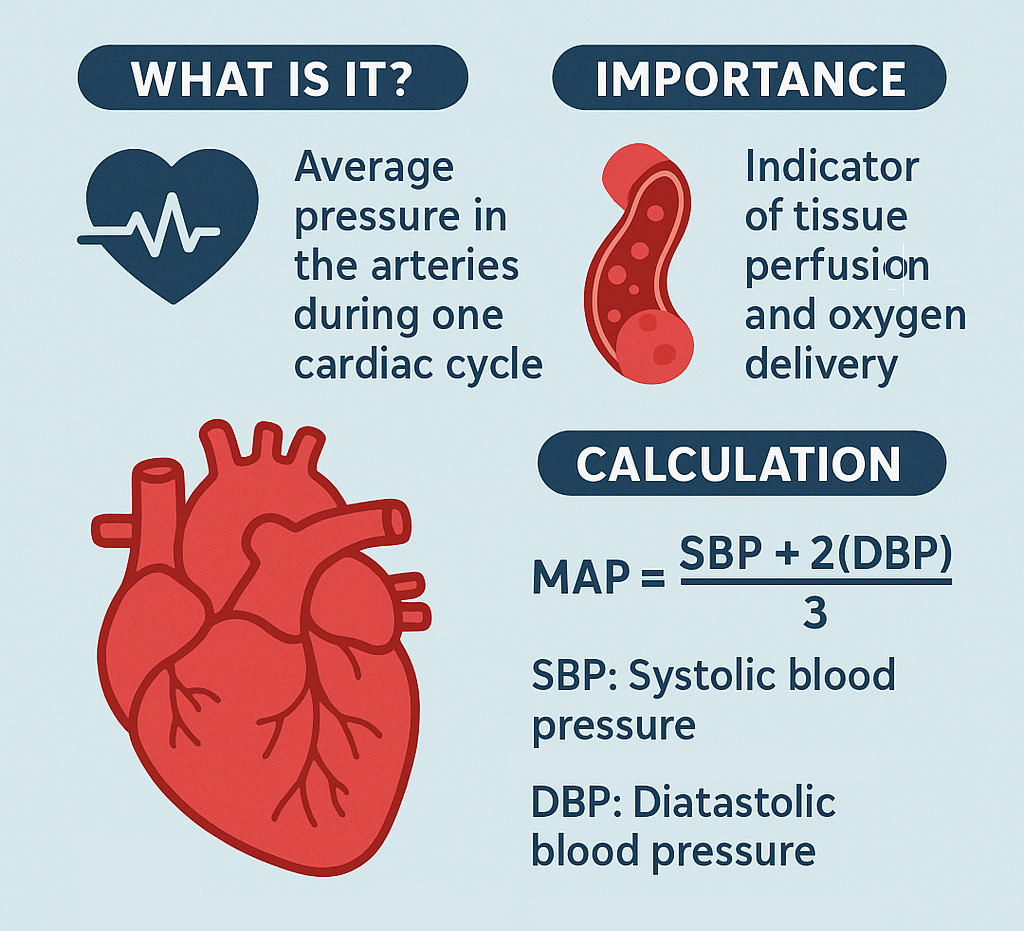
🫀 What is MAP?
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) represents the average pressure in your arteries during one complete heartbeat (cardiac cycle). It reflects the balance between systolic (when the heart pumps) and diastolic (when the heart relaxes) pressures.
🔎 Why is MAP Important?
MAP is a key indicator of how well your organs and tissues are receiving blood and oxygen.
- Too low → risk of poor perfusion (organs don’t get enough oxygen).
- Too high → extra strain on your heart, kidneys, and blood vessels.
Doctors often monitor MAP closely in critical care, dialysis, and kidney health management to ensure stability.
🧮 How is MAP Calculated?
MAP can be estimated using a simple formula:
MAP ≈ (SBP + 2 × DBP) ÷ 3
- SBP = Systolic Blood Pressure (the top number)
- DBP = Diastolic Blood Pressure (the bottom number)
👉 For example:
If your blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, then
MAP ≈ (120 + 2×80) ÷ 3 = 93 mmHg
A normal MAP for most adults is 70–100 mmHg.
📌 Key Takeaway
MAP provides a more reliable picture of organ perfusion than looking at systolic or diastolic blood pressure alone. Understanding MAP helps patients and caregivers recognize why blood pressure control is so critical in kidney care.
Please note that our articles are not intended to guide personal health decisions.
This content has been curated by Renes Care. Unauthorized use or reproduction is prohibited.
© Renes Care. All rights reserved.